 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
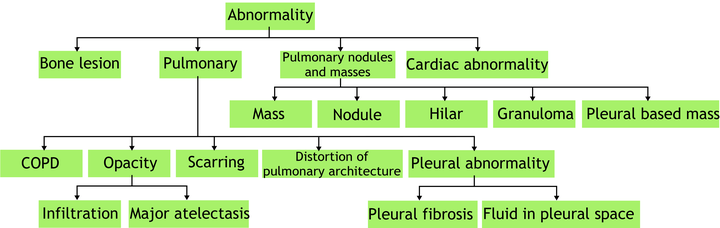
Chest X-rays (CXRs) are a crucial and extraordinarily common diagnostic tool, leading to heavy research for Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) solutions. However, both high classification accuracy and meaningful model predictions that respect and incorporate clinical taxonomies are crucial for CAD usability. To this end, we present a deep Hierarchical Multi-Label Classification (HMLC) approach for CXR CAD. Different than other hierarchical systems, we show that first training the network to model conditional probability directly and then refining it with unconditional probabilities is key in boosting performance. In addition, we also formulate a numerically stable cross-entropy loss function for unconditional probabilities that provides concrete performance improvements. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to apply HMLC to medical imaging CAD. We extensively evaluate our approach on detecting 14 abnormality labels from the PLCO dataset, which comprises 198,000 manually annotated CXRs. We report a mean Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.887, the highest yet reported for this dataset. These performance improvements, combined with the inherent usefulness of taxonomic predictions, indicate that our approach represents a useful step forward for CXR CAD.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code, math, and images.